![]() 2023/03/10 | MMDInnovationHub
2023/03/10 | MMDInnovationHub
Until the late 2000s, the standard aspect ratio among monitors was 4:3. It was known then as 'fullscreen'. That meant boxy displays to view films and broadcasts produced in the same format during that time.
Displays then took a rectangular form, and the aspect ratio transitioned to 16:9, which became known as 'widescreen'.
What is aspect ratio in monitors? It simply refers to the correlation between the width and height of a display. The higher the numbers, the wider the screen.
HD evolving
With more content produced in high definition, 16:9 became the standard. Think DVDs, film and television, as well as video games.
High definition (HD) became ultra-high definition and Quad HD, and the standard went up another level in aspect ratio - 21:9. However, its use is limited to UltraWide monitors and television screens.
Already, there is a 32:9 aspect ratio to accommodate SuperWide screens, the display sizes of which are at least 45", if not higher.
 The standard aspect ratio has increased over time – from 16:9 to 21:9 to 32:9 – following the evolution of HD imaging.
The standard aspect ratio has increased over time – from 16:9 to 21:9 to 32:9 – following the evolution of HD imaging.
Why wide screen?
Extreme gaming enthusiasts enjoy a more immersive player experience with an UltraWide display, but who else needs these wide screens?
Creative professionals working with graphics, videos, animation, and even music, will increase productivity when they switch to monitors with 21:9 or even 32:9 aspect ratios.
The bigger the display, the more they can work while reducing the steps to complete a task. And the higher the aspect ratio, the more pixels are visible, resulting in enhanced clarity of images.
Imagine this: multiple tabs open side-by-side, so there is no need to switch views from one document or program to another. Sometimes, even 21:9 is not enough for users with a heavy workload. But it can help do away with a multiple-monitor setup, saving on workspace.
Besides, sitting in front of a monitor for extended periods can cause eye fatigue, especially if staring at small figures or visuals that could be sharper with more vibrant colors.
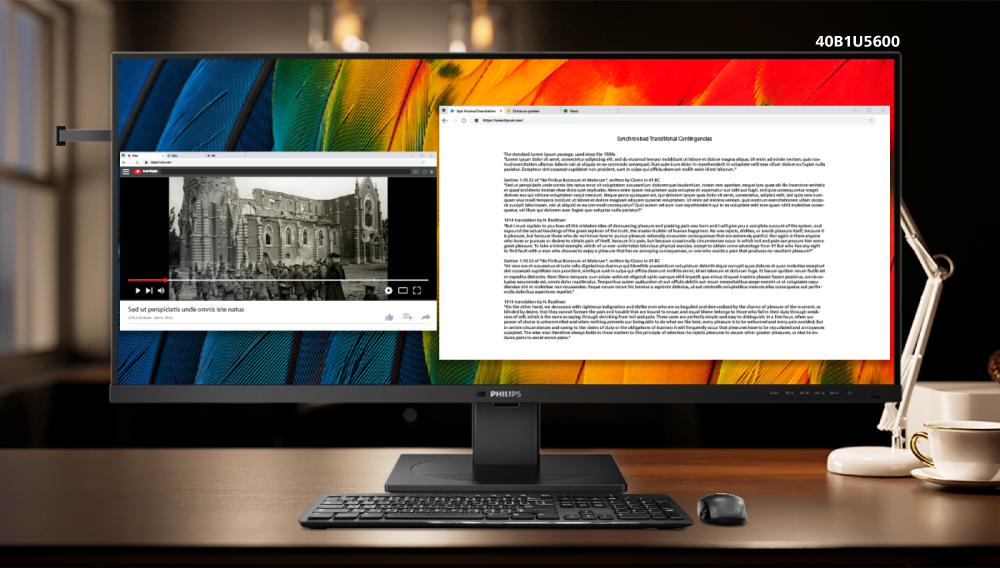 Philips Monitors 40B1U5600 was designed for business to allow viewing multiple tabs side-by-side.
Philips Monitors 40B1U5600 was designed for business to allow viewing multiple tabs side-by-side.
A wider screen enhances image quality because higher resolution reduces or eliminates eye strain.
So, which UltraWide monitor suits your needs? Philips Monitors offers an array of models beyond widescreen.
The wider, the clearer
Two of these are among the widest in the category, with sizes ranging between 40" to 45". Both fall under the business monitor line - 40B1U5600 and 45B1U6900CH.
The 40" is an UltraWide display with a 3440 x 1440px resolution (WQHD). It allows extra viewing angles and provides crisp images with vivid colors appreciated not only by gamers.
Meanwhile, the 45B1U6900CH is a unique monitor not only for its size and 32:9 aspect ratio but also for its curved design.
Curved displays provide an immersive effect as the eyes focus on the entire screen, including peripherals, so it takes everything in all at once.
This model also boasts Dual QHD resolution with 5120 x 1440px and is VESA-certified for DisplayHDR™ 400, which is already an assurance for vibrant colors and sharper images.
Like the 40B1U5600, the slightly smaller 346E2LAE has a 3440 x 1440px resolution, referred to as WQHD. The UltraWide monitor (21:9) features the CrystalClear technology for detailed information invaluable for CAD-CAM solutions and even complicated spreadsheets.
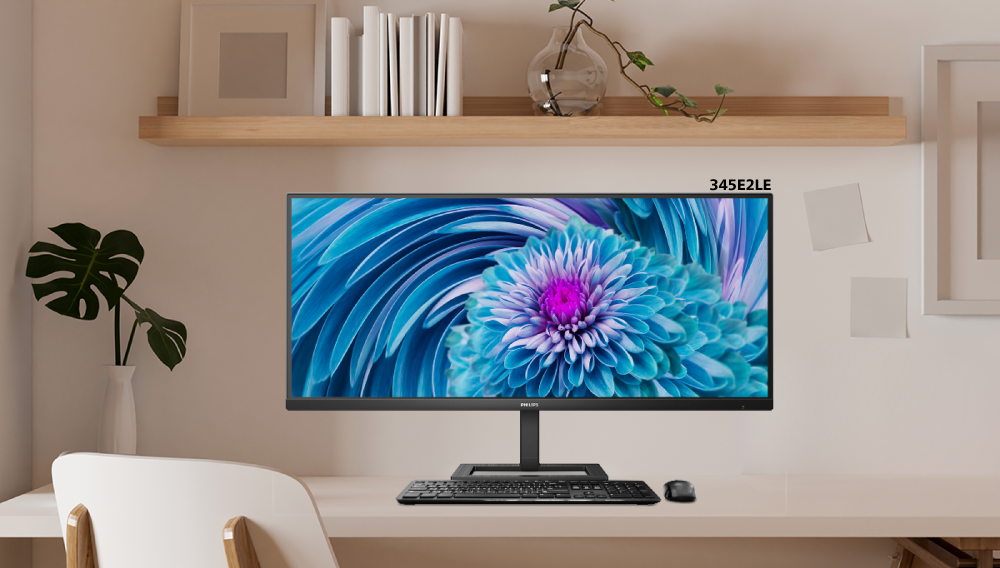 Philips Monitors 345E2LE offers an UltraWide view for an expansive viewing experience.
Philips Monitors 345E2LE offers an UltraWide view for an expansive viewing experience.
The other 21:9 display is the 34" 345E2LE model that like its 40" counterpart model, has a WQHD resolution (3440 x 1440px) and a refresh rate of 100Hz.
Another feature is the SmartContrast, a Philips Monitors technology that analyzes contents and automatically adjusts colors while controlling backlight intensity.
All four models also share a common feature - a USB-C port. Plugging a single cable allows viewing a high-resolution video, transferring data, and charging a compatible device simultaneously.
Using a wide screen not only for gaming is not bragging. It has more useful purposes that can make sitting in front of a monitor much more convenient and productive.